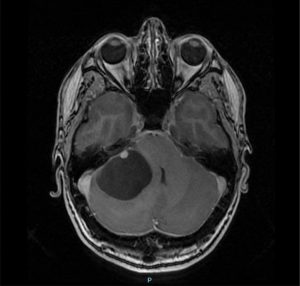
These are benign tumours originating from blood vessel cells. In the majority of cases they have a cystic component, the result of transudate through diseased capillaries. The most common location is at a level of the posterior fossa (cerebellum), although cases have also been described at a supratentorial and medullary level.
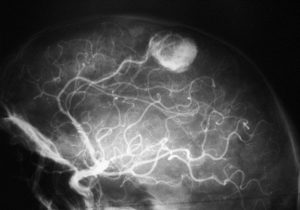 They may appear sporadically or associated with Von Hipple-Lindau disease in approximately 20% of cases.
They may appear sporadically or associated with Von Hipple-Lindau disease in approximately 20% of cases.
Von Hipple-Lindau disease: this is an autosomal dominant syndrome with a penetrance of 90%, it is an uncommon condition associated with the presence of tumours of the nervous system, renal cell carcinoma, pheochromocytomas, etc.
Diagnosis:
Once again diagnosis requires medical imaging with MRI being of choice, up to 70% present a cystic component. In these cases, it is important to note that the walls of the cyst are not tumoural, and so it will not be necessary to resect them during surgery.
Treatment:
Surgery will be the treatment of choice. In single lesions, resection of the nodule will be curative. In cases of multiple lesions, the number of lesions to be resected must be selected before surgery since any below 1 cm in diameter may be difficult to find and resect.