Colloid cysts are benign lesions that generally originate in the anterior part of the third ventricle, although they may be located in other areas such as the Septum pellucidum. Although biologically benign, their location may cause acute obstruction of the cerebrospinal fluid drainage system which leads to a sudden rise in intracranial pressure and as a result a potentially life-threatening situation.
These are infrequent lesions, in many cases asymptomatic, especially if they small in size (less than 1.5 cm diameter). When they appear the clinical signs are generally due to increased intracranial pressure, causing headache, gait disorders, vomiting, vision loss, etc.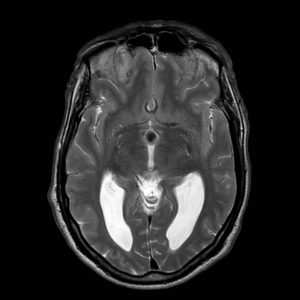
Diagnosis
This requires imaging tests with cerebral MRI being that of choice as it enables delimiting the anchor area of the cyst with greater precision.
Treatment:
In symptomatic cases or lesions that have reached a certain size, the treatment of choice will be surgical resection.
This may be performed by craniotomy and resection of the lesion, or using endoscopic resection. All that is required for this procedure is a cranial trepan.



